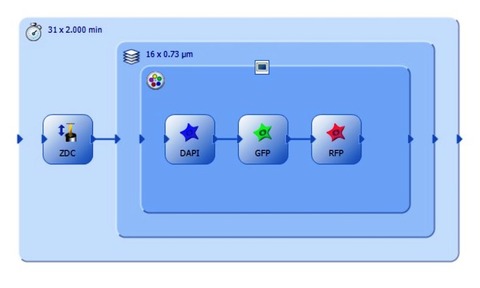
With Olympus’ GEM interface integrated into the latest release of the cellSens imaging software, executing the most intricate life science imaging experiments is possible with ease and efficiency.
Personalised automation is the key to managing complex multi-dimensional experiments, and the latest Olympus cellSens imaging software (version 1.11) seamlessly controls motorised hardware to allow effortless set-up of complex acquisition sequences and protocols, the company claims.
The Graphical Experiment Manager (GEM) interface allows the user to “draw” their experimental schematic on-screen with familiar “drag and drop” actions, enabling complete control and experimental set-up of motorised components and accessories with almost no need for training.
The capabilities of this interface are now expanded to the control of motorised stages, enabling the easy automation of multi-position experiments such as individual scanning protocols performed at different positions on a multi-well plate.
Providing insights into a host of biological processes, additional new features of the software include online ratiometric analysis, delivering results in real time and control of rapid focusing devices for fast 3D applications, while also supporting the latest cameras and image-splitter components.
From image acquisition to analysis, expanding the range of components compatible with cellSens presents new avenues of exploration within life science.
Additional models of EMCCD and sCMOS cameras are now supported such as the Hamamatsu ImagEM X2 and the Andor Zyla 4.2, delivering rapid and sensitive imaging; while 3D applications benefit from the integrated control of piezo-driven devices, for ultra-fast Z-stacking and focusing.
Multi-channel imaging of samples with fast dynamics is now supported through the use of an image splitter, with up to four emission channels acquired at the same precise moment.
The exact synchronisation of multiple wavelengths also quickly produces reliable images for advanced applications such as FRET and ratiometric analysis.
Moreover, ratiometric analysis can now be achieved “online”, enabling the real-time tracking and updating of ratiometric images and graphs during experiments.





