Metrohm describes the determination of boric acid in nuclear reactors.
Boric acid is used in nuclear power plants to slow down the rate at which fission is occurring.
Fission chain reactions are generally driven by the amount of neutrons present (as products from previous fissions).
By adding more boric acid to the reactor coolant that circulates through the reactor, the probability that a neutron can survive to cause fission is reduced.
Therefore, boric-acid concentration changes effectively regulate the rate of fissions taking place in the reactor.
This is only done in pressurised water reactors.
Boron is also dissolved into the spent fuel pools containing used uranium rods.
The concentration is high enough to keep neutron multiplication at a minimum.
The boric-acid content in the primary cooling system of light water reactors can be determined potentiometrically.
In pressure reactors boric acid is used as a safety reserve when the reactor is switched off.
In addition, boron is used to compensate the difference in reactivity and, more recently, for output regulation.
In the potentiometric determination of boric acid this is treated with a polyvalent alcohol.
The complex compound formed behaves like a monovalent medium-strength acid and can be titrated with sodium hydroxide.
Reagents used are sodium-hydroxide solution, c(NaOH) - 0.1mol/L (or more diluted) as the titrant, and D-Mannitol solution, c(mannitol) - 10 per cent in distilled Water.
The analysis is carried out by pipetting a defined volume of the sample into a plastic beaker, add 30ml distilled water and 10ml c(mannitol) - 10 per cent and titrate with c(NaOH) - 0.1mol/l.
Two equivalence points are obtained, the first of which corresponds to the HBF4 content and the difference between the second and the first equivalence point to the H3BO3 content.
1ml c(NaOH) - 0.1mol/l corresponds to 8.781mg HBF4 or 6.183mg H3BO3.
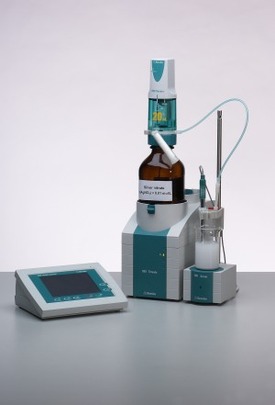
Using an 809 Titrando in conjunction with the 2x800 Dosino dosing systems, the titration of boric acid can be carried out automatically, as one burette adds the mannitol and the other one titrates with NaOH.
The instrument is controlled using the full-colour 840 touch control.
The indicator electrode used is the Metrosensor unitrode, a combined pH glass electrode with an easy-to-clean diaphragm, which is designed specifically for demanding titrations.





