Research from scientists at Peak Scientific suggests that the use of hydrogen in gas chromatography (GC) is safe.
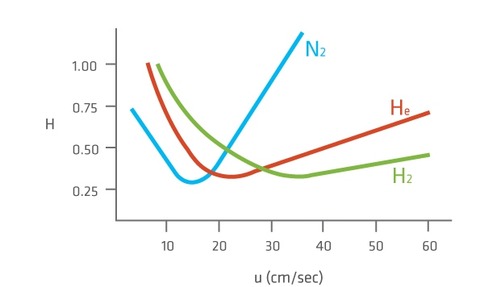
Historically, helium has been the gas of choice in most GC applications as hydrogen can pose various safety risks and nitrogen is less efficient.
Researchers from Peak Scientific have recently discussed the potential shortage of helium, and the need to find a suitable replacement for the increased demand within the medical, scientific and industrial fields.
Though researchers have stated that the risks of hydrogen can be higher than that of helium or nitrogen, they have outlined the benefits of using the gas in GC applications.
The research suggested that faster liner flow rates allow for shorter running times, increasing laboratory throughput and with a faster elution rate, the researchers believe it may be possible to operate at a lower temperature when performing analysis.
A further advantage is the availability of hydrogen and the ability to produce hydrogen supplies via the electrolysis of water, making it readily accessible.
Arguing against the use of pressurised hydrogen cylinders, the researchers believe contaminants are introduced when gas is changed from cylinder to cylinder; potentially reducing the quality of analysis and results.
The researchers argued that a gas generator eliminates the potential risk of contamination, whilst reducing the explosive nature of hydrogen as it is not stored within a pressurised container.
Concluding with the fact that hydrogen is a cheaper alternative to helium and a faster reactant than nitrogen, the scientists believe GC applications can be safely enhanced when used with a hydrogen generator, rather than a pressurised cylinder.
To read the reserach note, click on the link above.




