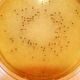
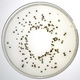
These antibody-coated microscopic paramagnetic beads are used for the rapid immunomagnetic separation of the micro-organism under test, eliminating the need for traditional enrichment processes
Lab M's innovative Captivate immunomagnetic separation (IMS) products and methodology are being used to enhance and accelerate a range of microbiological processes.
In food applications, for example, Captivate can reduce the time required for total viable counts, allowing rapid achievement of a presumptive negative for pathogens.
This can be particularly important in the isolation of Escherichia coli O157:H7 from meat and milk samples.
As well as Escherichia coli O157:H7, the range includes Captivate for other E coli serotypes and salmonella isolation.
Lab M also offers a custom coating service.
Captivate beads consist of a magnetite core enveloped by a ceramic zirconium oxide coating and have an average size of 2.5um.
Each Captivate product is designed for the specific target bacteria and pre-coated with the relevant antibody.
When mixed with a sample suspension and incubated, the antibody-coated beads bind to cell surface antigens forming an antibody-antigen complex with the target molecules.
The target bacteria are said to be 'captured'.
A magnetic concentrator is used to separate the complexes from any background organisms or interfering materials.
Subsequent washing removes non-specifically bound material and the beads can be plated to the appropriate selective media or used in other analyses.